In gasoline engines and natural gas engines, the throttle body is the core component of the intake system. Its main function is to control the flow of air or mixed gas into the engine, thereby affecting the relevant performance indicators of the engine. During long-term use, the throttle body will experience position sensor signal drift, aging of the return spring, carbon deposits, and foreign matter jams. In the above cases, the ECU can only detect the fault when a serious fault occurs. For minor faults or If an abnormality is not discovered in time, it will further affect the relevant performance indicators of the engine, such as insufficient power and increased fuel consumption.
In response to the above problems, this paper designs a detection section.
The method of abnormal body is to find the problem early and remind the user.
Fault detection method
The main technical solution is to use a certain algorithm to verify the degree of difference in intake air flow under different calculation methods, and to further reflect whether the current throttle is normal. The specific implementation plan is as follows: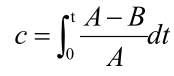
(1) Define the intake air flow calculated with the related parameters of the throttle as variable A. The specific value of A is calculated by the throttle formula based on the throttle opening, the pressure difference between the front and rear of the throttle, and the throttle diameter. The actual intake air flow actually collected and calculated by the flow sensor or the post-throttle pressure sensor is defined as variable B.
(2) This paper uses the actual flow rate B calculated by the flow sensor or the post-throttle pressure sensor as the accurate value to verify the validity of the variable A, so as to deduce whether the throttle is abnormal.
(3) Detection mechanism: Under normal circumstances, variables A and B are almost equal. If the deviation factor C of A and B within a certain period of time is greater than or equal to the standard value 1 or less than or equal to the standard value 2, it means that the throttle is abnormal. The fault needs to be triggered to remind the user to overhaul or maintain.
(4) The deviation factor calculated by variables A and B is defined as C, which means the integral cumulative value of the ratio of the difference between A and B to the target A, which is used to reflect the deviation between the two within a certain time t, and its calculation method as follows:
Where t is the time when the integral function is enabled each time. The initial value of the variable C is set to 1, and the variable is stored in the EEPROM every time T15 is powered off, and the value is read from the EEPROM after the next power on to participate in the integral operation.
(5) In some specific working conditions, such as the start-up phase, low-load working conditions and related sensor failures, the flow A, B itself has a certain deviation, in order to avoid such working conditions from affecting the judgment of failure and integration, Therefore, the fault judgment and the integral of the deviation factor C are added to the enabling condition D. When the enabling condition D is met, the fault detection and integral calculation are enabled. The enabling condition D mainly includes: ①The engine speed is within a certain range; ②No knots Body related failures; ③The temperature, pressure and flow sensor failures before and after the throttle; ④The accelerator pedal opening is greater than a certain value, etc.
Post time: Dec-03-2021